Directional Drilling: Engineering the Future of Subsurface Access

Directional drilling has emerged as a groundbreaking technique that is reshaping how we access and utilize underground resources. Unlike traditional drilling methods that typically involve a straight borehole, directional drilling allows for more versatility, enabling operators to drill at various angles and depths. This innovation is critical for industries such as oil and gas, public services, and renewable energy, where accurate and effective access to underground assets is paramount. As urban landscapes continue to expand and the demand for ecologically-friendly infrastructure grows, directional drilling stands at the cutting edge of engineering solutions that reduce surface disruption and enhance project efficiency.
Over the years, the evolution of directional drilling technology has been nothing short of impressive. From its modest beginnings to the advanced methods and equipment we see today, this drilling approach has continually evolved to meet the needs of contemporary projects. Understanding the different types of directional drilling, such as horizontal and upright drilling, is essential for experts and enthusiasts alike. By exploring the principles and uses of this technology, we can appreciate how directional drilling not only optimizes resource extraction but also plays a significant role in supporting urban infrastructure and environmental sustainability.
Types and Applications of Directional Boring
Directional boring encompasses various techniques tailored to meet particular project needs. The primary types include horizontal drilling, which enables for drilling parallel to the earth's surface, and vertical boring, which goes downward. Other methods, such as multi-lateral drilling, facilitate multiple wellbores to be drilled from a sole parent well, enhancing reservoir access. Each type serves unique purposes, ensuring the most efficient search and retrieval of resources.
In the oil and gas industry, directional boring is essential for accessing hard-to-reach reserves without the need for extensive surface disruption. This method has revolutionized how companies approach the extraction of resources by limiting environmental impact while boosting output. Beyond fossil fuels, directional boring is equally vital in the utility sector, where it facilitates the installation of pipe installations and cables underground, minimizing surface disturbances in urban areas.
Sustainable energy projects are also taking advantage of directional drilling to enhance site access and resource extraction. Whether installing geothermal wells or installing wind farm foundations, this technology supports green energy initiatives while preserving the integrity of surrounding ecosystems. As industries continue to expand, the versatility and adjustability of directional boring ensure it remains a crucial component in modern engineering and infrastructure development.
Advantages and Advantages of Directional Drilling
Directional boring offers significant advantages over conventional drilling methods, primarily in terms of productivity and precision. By enabling drillers to drill at different angles, it allows access to reserves that would be difficult or hard to reach with straight drilling by itself. This capability not only maximizes material extraction but also minimizes the number of drilling locations needed, thus lessening ecological effects and inconveniences to the surrounding area.
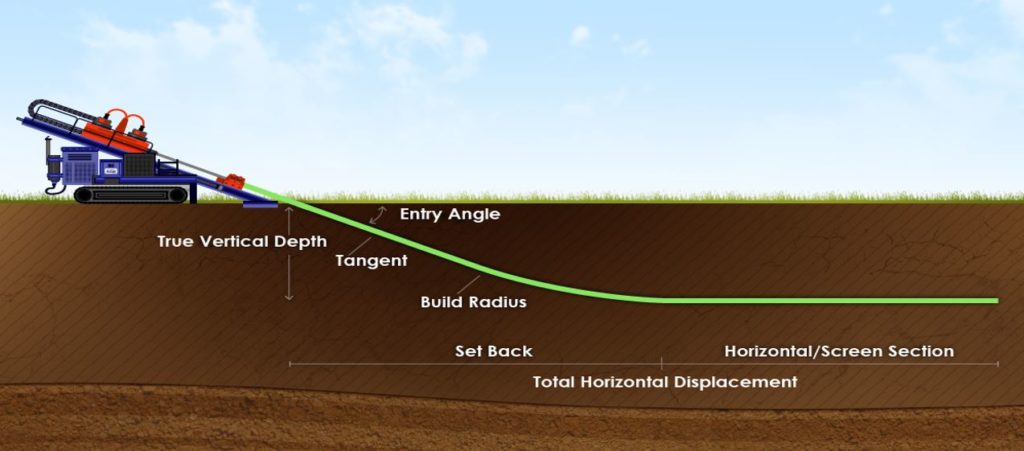
Moreover, horizontal boring drastically reduces ground disruption. This is particularly beneficial in city environments where room is scarce and the risk of harming existing infrastructure is elevated. The capability to navigate around barriers ensures that drilling can occur beneath streets, buildings, and other structures without the need for extensive surface excavation or demolition, preserving the stability of the city landscape.
In addition to saving time and costs, horizontal drilling is increasingly recognized for its environmental advantages. The method reduces land utilization and reduces the greenhouse gas impact associated with boring operations. Furthermore, its precision helps steer clear of sensitive ecological areas, ensuring that projects align with sustainability objectives. As Click This Link continue to focus on -friendly approaches, horizontal boring stands out as a vital technique for upcoming projects.
Emerging Trends in Directional Drilling Techniques
As the need for more efficient and minimally disruptive drilling techniques grows, the future of directional drilling methods looks encouraging with several emerging advancements. One of the most significant developments is the incorporation of artificial intelligence and automated systems into drilling operations. These tools are improving drilling accuracy, allowing for real-time data analysis and flexible decision-making during drilling projects. This allows for operators can adjust their strategies on the fly, resulting to quicker completion times and reduced costs.
Another exciting trend is the use of cutting-edge software and sensor technology. These tools provide enhanced monitoring capabilities, allowing for improved bore tracking and safety assessments. The evolution of data analytics will allow operators to predict drilling difficulties before they occur, further optimizing project outcomes. This combination of smart technology and conventional engineering methods is set to revolutionize how directional drilling operations are managed and executed.
Lastly, the shift towards sustainability is influencing the future landscape of directional drilling. Techniques that reduce ecological impact are becoming increasingly important, especially in vulnerable locations. Innovations like eco-friendly drilling fluids and processes designed to further reduce surface interference are critical for adhere to regulatory standards and community expectations. As the industry adopts these green practices, directional drilling is poised to play a key role in supporting the development of facilities that is both effective and environmentally responsible.
